Welcome!
In 2000, the Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory (SPSC Lab) of Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) was founded as a research and education center in nonlinear signal processing and computational intelligence, algorithm engineering, as well as circuits & systems modeling and design. It covers applications in wireless communications, speech/audio communication, and telecommunications.
If you want to learn more about Signal Processing, click: What is Signal Processing?
The Research of SPSC Lab addresses fundamental and applied research problems in five scientific areas:
- Audio and Acoustics
- Intelligent Systems
- Nonlinear Signal Processing
- Speech Communication
- Wireless Communications
Profiles
Result of the Month
Mean- and Median-Based Outlier Testing
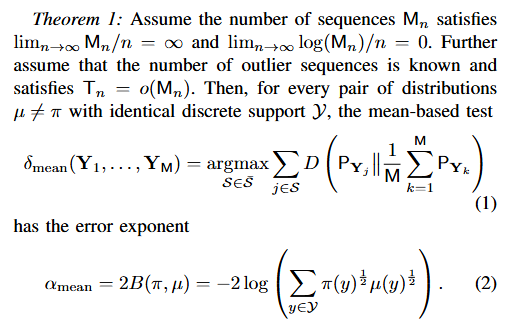
In this study, we revisit the classical problem of identifying outlier sequences from a large set of sequences when neither the typical distribution nor the outlier distribution is known a priori (universal setting). Assuming that the number of sequences grow faster than the sequence lengths, we introduce and analyze two simple yet powerful test statistics — mean‐based and median‐based estimators — that are computationally tractable and whose errors decrease exponentially with the sequence length.
Read the full article.Contact: Bernhard Geiger