Automatic Pitch Accent Annotation of Conversational German
- Status
- Finished
- Type
- Bachelor Project
- Announcement date
- 08 Oct 2023
- Students
- Maximilian Karner
- Adam Toeroek
- Mentors
- Research Areas
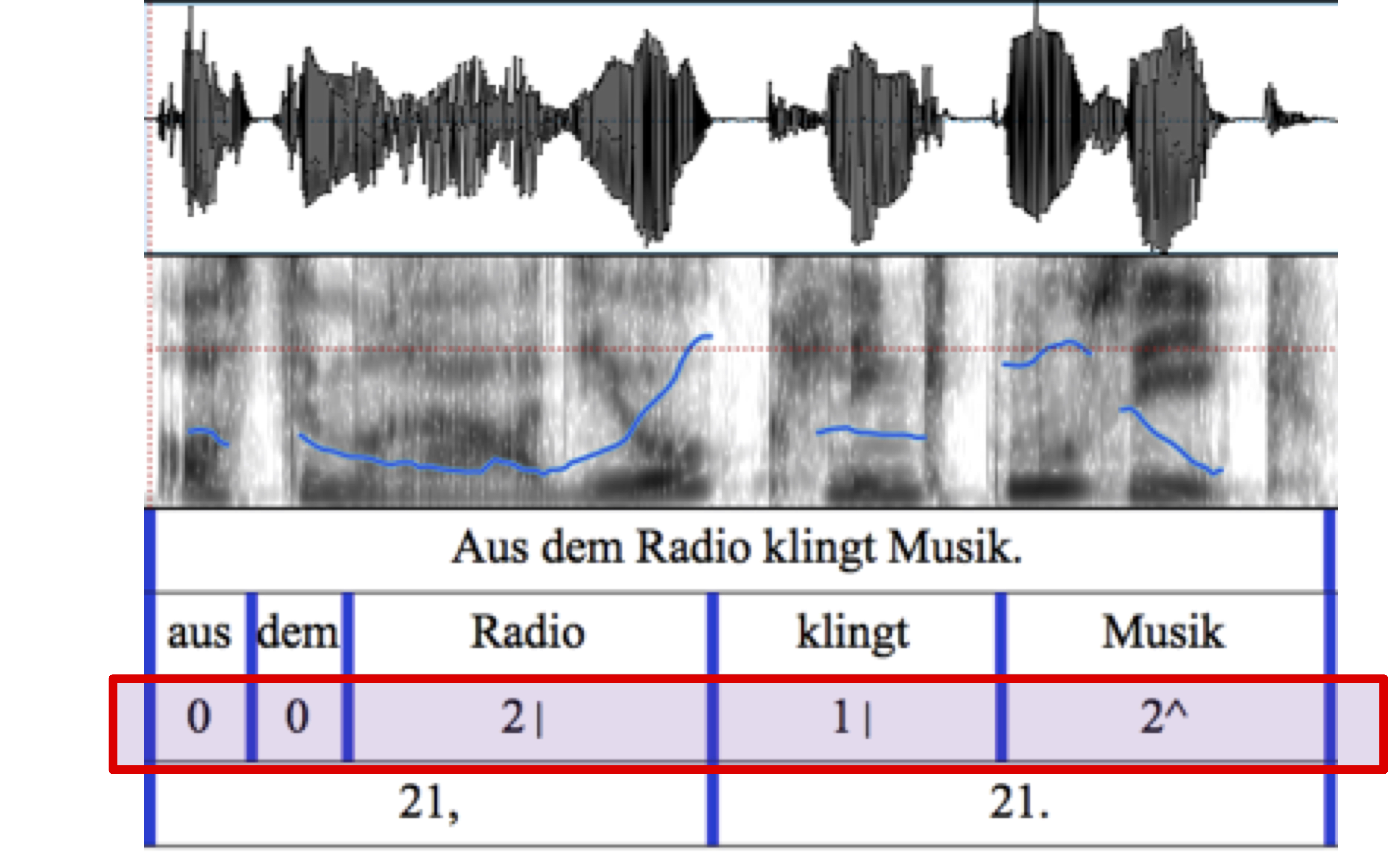
The nature of conversational speech compared to read speech poses a significant challenge for Automatic Speech Recog- nition (ASR) systems. There are several existing studies that focus on improving the performance of ASR by us- ing prosodic features. The accurate annotation of prosodic characteristics like stress and intonation is a key part of this process. This bachelor project focuses on categorizing words into different pitch accent classes according to the Kiel Intonation Model (KIM), and investigates the influence of diverse acoustic features on the accuracy of the classification, focusing on the impact of entropy-based chroma features. The classification experiments consist of training and testing a Random Forest classifier with multiple combinations of pitch accent categories and features, and comparing them based on their impact on classification performance. The experiments show that classical prosodic features generally outperform chroma features in pitch accent classification, with F0-based features being the most important. The highest classification accuracy was achieved in binary classification tasks involving semantically distinct classes, followed by groupings based on semantic-functional similarity. Groupings based on contour shapes delivered moderate performance, with entropy based chroma features showing minimal impact across all setups.