On Multiangle Discrete Fractional Periodic Transforms
- Published
- Sun, Feb 01, 2026
- Tags
- rotm
- Contact
Fractional transforms such as the discrete fractional Fourier transform (DFRFT) are important tools in digital signal processing, as they are used for data compression, cryptography and watermarking, linearly frequency modulated (LFM) chirp estimation, processing optical systems, among other applications. Many of these applications require computing multiple transforms of different fractional orders; in the context of interfered radar signals, for instance, DFRFTs of different fractional orders pulse-compress LFM chirp interferences with different chirp rates, enabling their mitigation.
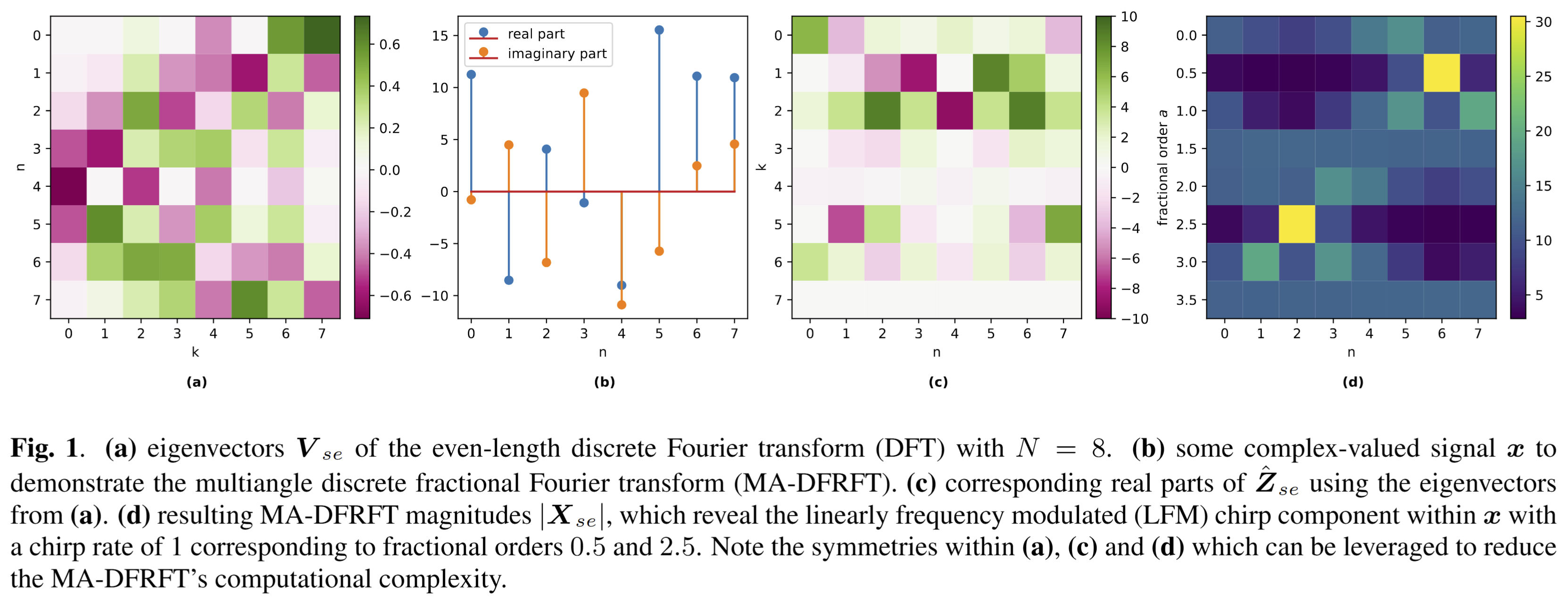
The multiangle centered discrete fractional Fourier transform (MA-CDFRFT, Vargas-Rubio & Santhanam, IEEE SPL 12(4):273-276, 2005) utilizes FFTs to efficiently compute the CDFRFT in parallel for multiple fractional orders. In this work, we generalize the MA-CDFRFT to arbitrary M-periodic transforms; more concretely, we reduce the computational complexity of all multiangle fractional M-periodic transforms from O(N^3) to O(N^2 log N). We do this by generalizing the method by Vargas-Rubio & Santhanam to arbitrary period-lengths M, eigenvalue exponents and eigenvectors. Our generalization now includes the fractional extensions of important transforms such as discrete Fourier, type-I and type-IV discrete sine and cosine, Hadamard and discrete Hartley transforms, among others. Furthermore, we exploit the symmetries inherent to the MA-CDFRFT and our novel multiangle discrete fractional Fourier transform (MA-DFRFT) to halve the number of FFTs needed to compute these transforms, which paves the way for applications in resource-constrained environments.
Our paper was accepted for presentation at the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 2026 and is available on arXiv.
Browse the Results of the Month archive.