Information-Criterion-Based Agent Selection for Cooperative Localization in Static Networks
- Published
- Sat, Aug 01, 2020
- Tags
- rotm
- Contact
In this work, we propose a Bayesian agent network planning algorithm for information-criterion-based measurement selection for cooperative localization in static networks with anchors. This allows to increase the accuracy of the agent positioning while keeping the number of measurements between agents to a minimum. The proposed algorithm is based on minimizing the conditional differential entropy (CDE) of all agent states to determine the optimal set of measurements between agents. Such combinatorial optimization problems have factorial runtime and quickly become infeasible, even for a rather small number of agents. Therefore, we propose a Bayesian agent network planning algorithm that performs a local optimization for each state. Experimental results demonstrate a performance improvement compared to a random measurement selection strategy, significantly reducing the position RMSE at a smaller number of measurements between agents.
The full version of the paper can be found on Researchgate
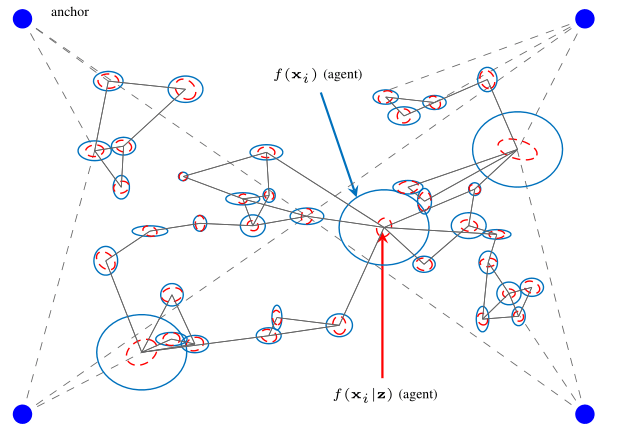
Figure: This figure shows a scenario of a static agent network with anchors (blue bullets) at known positions and cooperating agents, which have to be localized. Prior distributions due to measurements to anchors (dotted black lines) are indicated as blue ellipses. The selected links are depicted as black lines and the marginal posterior distributions due to the selected measurements between agents after the measurement update are given as red ellipses.
Browse the Results of the Month archive.