On Disfluency and Non-lexical Sound Labeling for End-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition
- Published
- Fri, Nov 01, 2024
- Tags
- rotm
- Contact
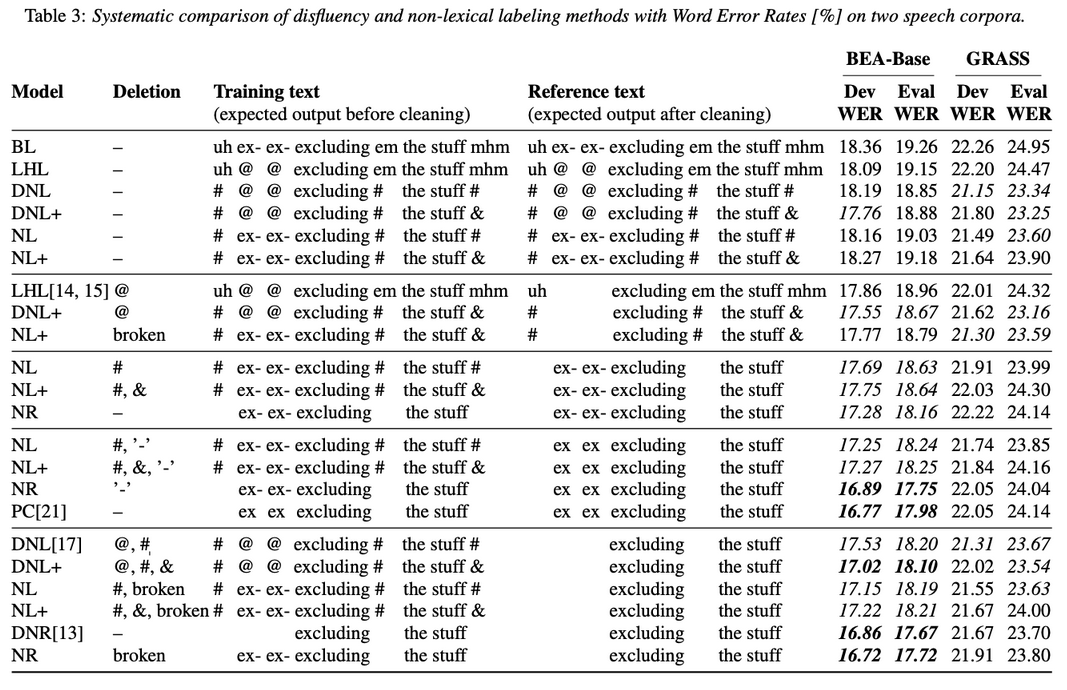
Abstract: Spontaneous speech contains a significant amount of disfluencies and non-lexical sounds (e.g., backchannels, filled pauses), which are often difficult to transcribe. Disfluency labeling for automatic speech recognition (ASR) aims at editing these phenomena in the transcription to improve overall recognition accuracy. Such labeling techniques typically delete nonlexical/disfluent labels from the prediction, where classical ASR techniques either ignore or treat them as lexical items. Our results, obtained by systematic comparison and detailed evaluation of various disfluency labeling methods on two different language conversational corpora, suggest that neither of the previous approaches are optimal. We propose to distinguish between filled pauses and meaningful conversational grunts and show that keeping the non-lexical labels is not only possible but as low as 7% label error rates can be achieved for highly important categories (including ’mhm’) while preserving a decent WER.
Index Terms: end-to-end speech recognition, disfluency, conversational speech, filled pauses, Hungarian, Austrian German
Konferenz: Proc. of Interspeech 2024, pp. 1270–1274, 2024. (1-5 September 2024, Kos, Greece)
Browse the Results of the Month archive.