Beamforming for Distant Speech Recognition in Reverberant Environments and Double-Talk Scenarios
- Published
- Fri, Jun 01, 2012
- Tags
- rotm
- Contact
Beamforming is crucial for distant-speech recognition to mitigate causes of system degradation, e.g., interfering noise sources or competing speakers. We introduced adaptations of state-of-the-art broadband data-independent and data-dependent beamformers to uniform circular arrays (UCA), such that competing speakers are attenuated sufficiently for distant speech recognition.
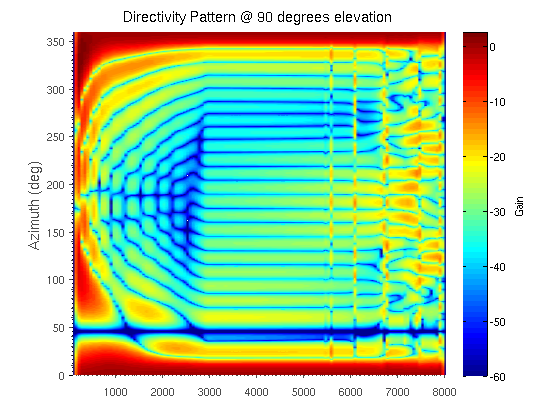
The newly introduced multiple null synthesis robust least squares frequency invariant beamformer (MNS-RLSFI) is a data-independent beamformer which enables null-placement in the directions of competing speakers. It is based on convex optimization methods that determine the weighting coefficients. The figure illustrates the directivity pattern of the MNS-RLSFI based on a 24-element UCA, a steering direction of 0 degrees, and a localized competing speaker at 45 degrees.
Our experiments show that data-independent beamformers feature a better performance than data-dependent beamformers in case of double-talk scenarios in reverberant environments. According to our results, the delay-and-sum beamformer is the most robust beamformer which exhibits the highest improvements in real-data scenarios, whereas the MNS-RLSFI outperforms all other beamformers in case of simulated free-field scenarios.
More information can be found in the Master Thesis.
Browse the Results of the Month archive.